Node 1
What we will learn today?
What is a server?
Servers are computer programs that receive requests from other programs, the clients and send back a response e.g share data, information or hardware and software resources.
...and what is a server in plain English?
A server is a computer program. Its job is to send and receive data.
Let's take a website for example. A website is just a collection of HTML and CSS files, images, maybe some javascript files. When you type a website address in your browser's address bar, the browser (client) sends a request to the server that lives at that address. The browser asks the server to give it the files it needs to display the website properly.

Node and its ecosystem
Node.js® is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine. Node.js uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model that makes it lightweight and efficient.
What is it used for?
- web servers, so creating dynamic websites
- set up a local web development environment
- easier to build desktop applications with Electron: Slack, Visual Code, Atom
- some of the biggest companies use Node.js in production: Netflix, Walmart, IBM, etc.
- JavaScript everywhere (used to be PHP, Python, JavaScript, MySQL, Apache, now JavaScript full stack)
A simple Node.js server
Simple server**
const http = require("http");
const server = http.createServer(function(req, res) {
res.end("Hello World!");
});
server.listen(5000);
console.log("Node.js web server at port 5000 is running..");
Server with two routes**
const http = require("http");
const server = http.createServer(function(req, res) {
if (req.url === "/") {
//check the URL of the current request
console.log("New request to main page at " + Date());
// set response header
res.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/html" });
// set response content
res.write("<html><body><h1>This is home Page.</h1></body></html>");
res.write("<h2>The time is: " + Date() + "</h2>");
res.end();
} else if (req.url === "/student") {
console.log("New request to Student page at " + Date());
res.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/html" });
res.write("<html><body><h1>This is student Page.</h1></body></html>");
res.end();
} else {
res.end(
"<html><body><h2>Invalid Request at " + Date() + "</h2></body></html>"
);
}
});
server.listen(5000);
console.log("Node.js web server at port 5000 is running..");
Exercise How would you add another route
/mentor?
HTTP
It is a protocol that browser and the server uses to talk to each other
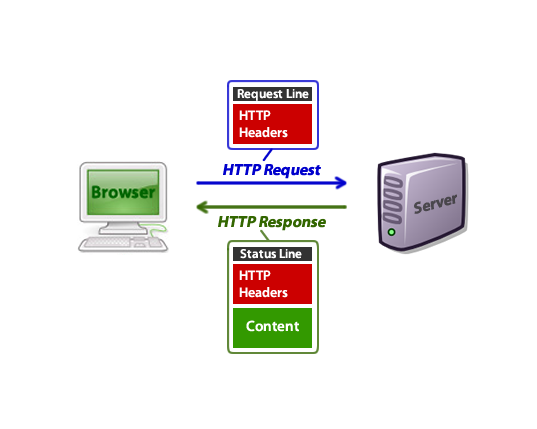
Read more on Mozilla's An overview of HTTP
Express
Express is one of the most widely-used frameworks for Node.js. It simplifies base features of Node.js, making it easier and faster to build your application's backend. Learning Express gives you a great foundation for becoming a Node.js developer.
In the next steps, we will building a CMS (Content Management System) - a
system to write, publish and save blog posts. Even though we could use core
libraries like http to build this system, this becomes very complicated and
non-maintainable very quickly. That is why we use frameworks like Express.
Workshop
Buckle up and start the express workshop.
Group Research Topics
- Security: (https, same origin, cookies, xss etc..)
- Performance: Request lifecycle (from browser to server and back), Performance considerations and optimisations
- HTTP and REST: (headers, status codes, Cookies, REST)
- Node internals: Node event loop, Node core modules, async/sync (non-blocking operations)
The research will be on a Github repo. One member of the group will be responsible of creating a repo, the others will fork it and create Pull Requests for it (that the main repo's owner will have to review and merge).
We expect each repo to have commits from each member of the group
Resources
Take a look at the following links to learn more about Node.js.
- Read: The art of node
- Read: Node Resources
More about HTTP: Tutsplus tutorial
More about JSON:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JSON
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/JSON/parse
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/JSON/stringify
Heroku:
Homework
- Finish the tasks from the workshop
- Try adding an
/aboutroute to your app to serve some HTML. How is this different from using express's static middleware? You can see one way of doing it here - Read & Practice: Express Middleware - Be prepared to name & describe at least 1 middleware at the class
- Learn about Templating Engines and make a simple page with Handlebars (with or without Express), and create a repository and post the link of your project on your card
- (Optional) Complete the nodeschool.io learnyounode tutorial
Escalation policy
When you get stuck during the homework you should follow the following:
- First, search for answers on Google and Stack Overflow. If you have an error message, copy and paste it into Google.
- When you are stuck for longer than 20 minutes - no longer! - write a question to your fellow students in your class channel on slack. Take a while to think carefully about the question. This is an important skill. Here is a great guide to writing good questions
- If you cannot get an answer from your fellow students,
post your question in your class public channel,
@the mentor for the class that covered the topic and we will reply as soon as we can.
